Periodontal disease, a common disorder that influences the gums and supporting tissues of the teeth, necessitates effective and personalized treatment treatment strategies. Gum disease is often treated using two methods: laser-aided new attachment procedure (LANAP) and assisted curetage. These procedures have the same goal of reducing periodontal diseases, but they differ in methodology, technology, outcomes, and patient experience. This article compares LANAP with assisted curettage to help patients and professionals understand the best gum disease treatment options.
For more intresting topic is : “daseiinno”
Understanding LANAP
Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure (LANAP) is an advanced, barely encroaching treatment for gum disease. Developed with the support of cutting-edge laser technology, LANAP offers a modern difference to traditional surgical types . The PerioLase MVP-7 laser, clearly designed for this purpose, is used to remove contaminated tissue while preserving healthy gum tissue. LANAP stimulates the body’s natural allay processes to reborn bone and reattach gum tissues to the teeth.
Key Features of LANAP:
- Targeted Treatment: The laser absolutely prey swollen and allay gum tissue.
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike traditional surgery, LANAP does not need scalpels or sutures.
- FDA-Approved: It is the only laser treatment accepted by the FDA periodontal disease.
- Regenerative Focus: It cheers bone growth and tissue rebirth.
- Short Recovery: Patients experience less post-operative pain and faster healing.
LANAP is particularly successful for patients with moderate to acute gum disease, offering a solution that minimizes discomfort while further long-term oral health.
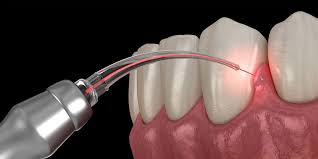
Understanding Assisted Curettage
Assisted curettage refers to a more traditional approved to treating periodontal disease. This experiment required scraping off diseased tissue from the periodontal pockets using hand instruments (curettes) or unhearable scalers. The term “assisted” implies the addition of adjunctive therapies such as antimicrobial rinses, antibiotics, or other chemical agents to increase treatment efficacy.
Key Features of Assisted Curettage:
- Manual Debridement: The physical removal of infected gum tissue plaque.
- Adjunctive Therapies: Use of antimicrobial or antigens agents to kill bacteria and low inflammation.
- Versatile Application: Can be used alone in conjunction with surgical treatments.
- Widely Available: A standard practice periodontal care due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Assisted curettage is often used for mild to moderate periodontal cases or as part of a maintenance program for ongoing periodontal health.
Key Differences Between LANAP and Assisted Curettage
| Aspect | LANAP | Assisted Curettage |
| Technology | PerioLase MVP-7 laser | Manual instruments with adjuncts |
| Procedure Type | Minimally invasive, laser-guided | Invasive, requires physical scraping |
| Recovery Time | Faster recovery, less discomfort | Slower recovery, potential swelling |
| Tissue Preservation | Selectively removes diseased tissue | Removes tissue indiscriminately |
| Focus | Regeneration of bone and tissue | Removal of infected tissue |
| FDA Approval | Yes | Not procedure-specific |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced technology | Lower, widely accessible |
| Target Cases | Moderate to severe periodontal disease | Mild to moderate periodontal disease |
Procedure and Patient Experience
LANAP Procedure:
- Initial Consultation: The dentist examines the severity of the gum disease and confirms usefulness for LANAP treatment.
- The PerioLase laser vaporizes sick gum tissue while leaving healthy tissue unaffected.
- Cleaning: Tartar deposits on the tooth surface can be moved with ultrasonic scalers.
- The laser stimulates gum tissue and bone to repair organically.
- Post-Treatment Care: Patients are urged to practice good oral hygiene and attend follow-up appointments.
Patients undergoing LANAP typically report minimal pain, reduced bleeding, and faster recovery. The experiment is ideal for those seeking effective treatment with minimal disruption to their daily lives.
Assisted Curettage Procedure:
- Initial Diagnosis: The dentist assesses the gum pockets’ drop and recognizes areas of infection.
- Tissue Moving : Curettes or ultrasonic tools are used to scrape off infected tissue and brass.
- Adjunctive Therapies: Antimicrobial agents or antibiotics are used to decrease bacterial loads and support healing.
- Follow-Up Treatment: For deeper pockets, additional sessions or surgical intervention may be required.
- Post-Treatment Care: Patients may experience tenderness and swelling,and need over-the-counter pain relief.
While assisted curettage is effective for less severe cases, its mechanical nature can lead to discomfort and slower healing contrast to LANAP.
Comparing Clinical Outcomes
LANAP Outcomes:
- Tissue Regeneration: Encourages the regrowth of bone and connective tissue.
- Long-Term Benefits: Higher success rates in maintaining periodontal health.
- Aesthetic Results: Preserves the natural gum line and reduces the risk of gum recession.
Assisted Curettage Outcomes:
- Effective Cleaning: Removes plaque and infected tissue effectively.
- Temporary Relief: Often requires additional treatments for long-term management.
- Risk of Tissue Loss: Can contribute to gum recession over time.
Cost Considerations
LANAP:
LANAP is more expensive since it uses sophisticated laser technology. The cost might vary from $1,000 to $4,000 each quadrant, depending on the location and degree of gum disease.
Assisted Curettage:
Compared to traditional treatments, assisted curettage is less expensive, usually costing between $200 and $300 per quadrant. Follow-up treatments or supplementary therapies may incur additional costs.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The decision between LANAP and assisted curettage depends on various factors:
- Severity of Disease: LANAP is better for advanced cases where regeneration is critical.
- Patient Comfort: LANAP offers a less invasive and more comfortable experience.
- Budget: Assisted curettage is more cost-effective but may require more frequent treatments.
- Desired Outcomes: Patients seeking long-term solutions and tissue regeneration may prefer LANAP.
Conclusion
Both LANAP and assisted curettage show important roles in periodontal therapy. LANAP leverages moderen laser technology to provide a minimally invasive, rebirth solution ideal for severe gum disease. In contrast, assisted curettage remains a reliable, cost-effective option for mild to low cases. Consulting with a skilled periodontist necessary to determine the most offensive treatment plan based on individual needs and oral health goals. Whether opting for the precision of LANAP or the traditional efficacy of assisted curettage, prioritizing timely and effective care is key to preserving oral health.
For more information about : Periodontal


